單眼深度估計
作者: Victor Basu
建立日期 2021/08/30
最後修改日期 2024/08/13
說明: 使用卷積網路實作深度估計模型。
簡介
深度估計是從 2D 圖像推斷場景幾何的關鍵步驟。單眼深度估計的目標是預測每個像素的深度值或推斷深度資訊,而僅以單一 RGB 圖像作為輸入。此範例將展示一種使用卷積網路和簡單損失函數來建構深度估計模型的方法。
設定
import os
os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = "tensorflow"
import sys
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
from keras import layers
from keras import ops
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
keras.utils.set_random_seed(123)
下載資料集
在此教學中,我們將使用資料集 DIODE:一個密集的室內和室外深度資料集。但是,我們使用驗證集來為我們的模型產生訓練和評估子集。我們使用驗證集而非原始資料集的訓練集的原因是,訓練集包含 81GB 的資料,這與僅有 2.6GB 的驗證集相比,下載起來更具挑戰性。您可以使用的其他資料集包括 NYU-v2 和 KITTI。
annotation_folder = "/dataset/"
if not os.path.exists(os.path.abspath(".") + annotation_folder):
annotation_zip = keras.utils.get_file(
"val.tar.gz",
cache_subdir=os.path.abspath("."),
origin="http://diode-dataset.s3.amazonaws.com/val.tar.gz",
extract=True,
)
Downloading data from http://diode-dataset.s3.amazonaws.com/val.tar.gz
2774625282/2774625282 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 205s 0us/step
準備資料集
我們僅使用室內圖像來訓練我們的深度估計模型。
path = "val/indoors"
filelist = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
for file in files:
filelist.append(os.path.join(root, file))
filelist.sort()
data = {
"image": [x for x in filelist if x.endswith(".png")],
"depth": [x for x in filelist if x.endswith("_depth.npy")],
"mask": [x for x in filelist if x.endswith("_depth_mask.npy")],
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=42)
準備超參數
HEIGHT = 256
WIDTH = 256
LR = 0.00001
EPOCHS = 30
BATCH_SIZE = 32
建立資料管道
- 該管道接受一個包含 RGB 圖像路徑以及深度和深度遮罩檔案的路徑的資料框架。
- 它讀取並調整 RGB 圖像的大小。
- 它讀取深度和深度遮罩檔案,處理它們以產生深度圖圖像並調整其大小。
- 它會傳回一個批次的 RGB 圖像和深度圖圖像。
class DataGenerator(keras.utils.PyDataset):
def __init__(self, data, batch_size=6, dim=(768, 1024), n_channels=3, shuffle=True):
super().__init__()
"""
Initialization
"""
self.data = data
self.indices = self.data.index.tolist()
self.dim = dim
self.n_channels = n_channels
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.shuffle = shuffle
self.min_depth = 0.1
self.on_epoch_end()
def __len__(self):
return int(np.ceil(len(self.data) / self.batch_size))
def __getitem__(self, index):
if (index + 1) * self.batch_size > len(self.indices):
self.batch_size = len(self.indices) - index * self.batch_size
# Generate one batch of data
# Generate indices of the batch
index = self.indices[index * self.batch_size : (index + 1) * self.batch_size]
# Find list of IDs
batch = [self.indices[k] for k in index]
x, y = self.data_generation(batch)
return x, y
def on_epoch_end(self):
"""
Updates indexes after each epoch
"""
self.index = np.arange(len(self.indices))
if self.shuffle == True:
np.random.shuffle(self.index)
def load(self, image_path, depth_map, mask):
"""Load input and target image."""
image_ = cv2.imread(image_path)
image_ = cv2.cvtColor(image_, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
image_ = cv2.resize(image_, self.dim)
image_ = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image_, tf.float32)
depth_map = np.load(depth_map).squeeze()
mask = np.load(mask)
mask = mask > 0
max_depth = min(300, np.percentile(depth_map, 99))
depth_map = np.clip(depth_map, self.min_depth, max_depth)
depth_map = np.log(depth_map, where=mask)
depth_map = np.ma.masked_where(~mask, depth_map)
depth_map = np.clip(depth_map, 0.1, np.log(max_depth))
depth_map = cv2.resize(depth_map, self.dim)
depth_map = np.expand_dims(depth_map, axis=2)
depth_map = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(depth_map, tf.float32)
return image_, depth_map
def data_generation(self, batch):
x = np.empty((self.batch_size, *self.dim, self.n_channels))
y = np.empty((self.batch_size, *self.dim, 1))
for i, batch_id in enumerate(batch):
x[i,], y[i,] = self.load(
self.data["image"][batch_id],
self.data["depth"][batch_id],
self.data["mask"][batch_id],
)
x, y = x.astype("float32"), y.astype("float32")
return x, y
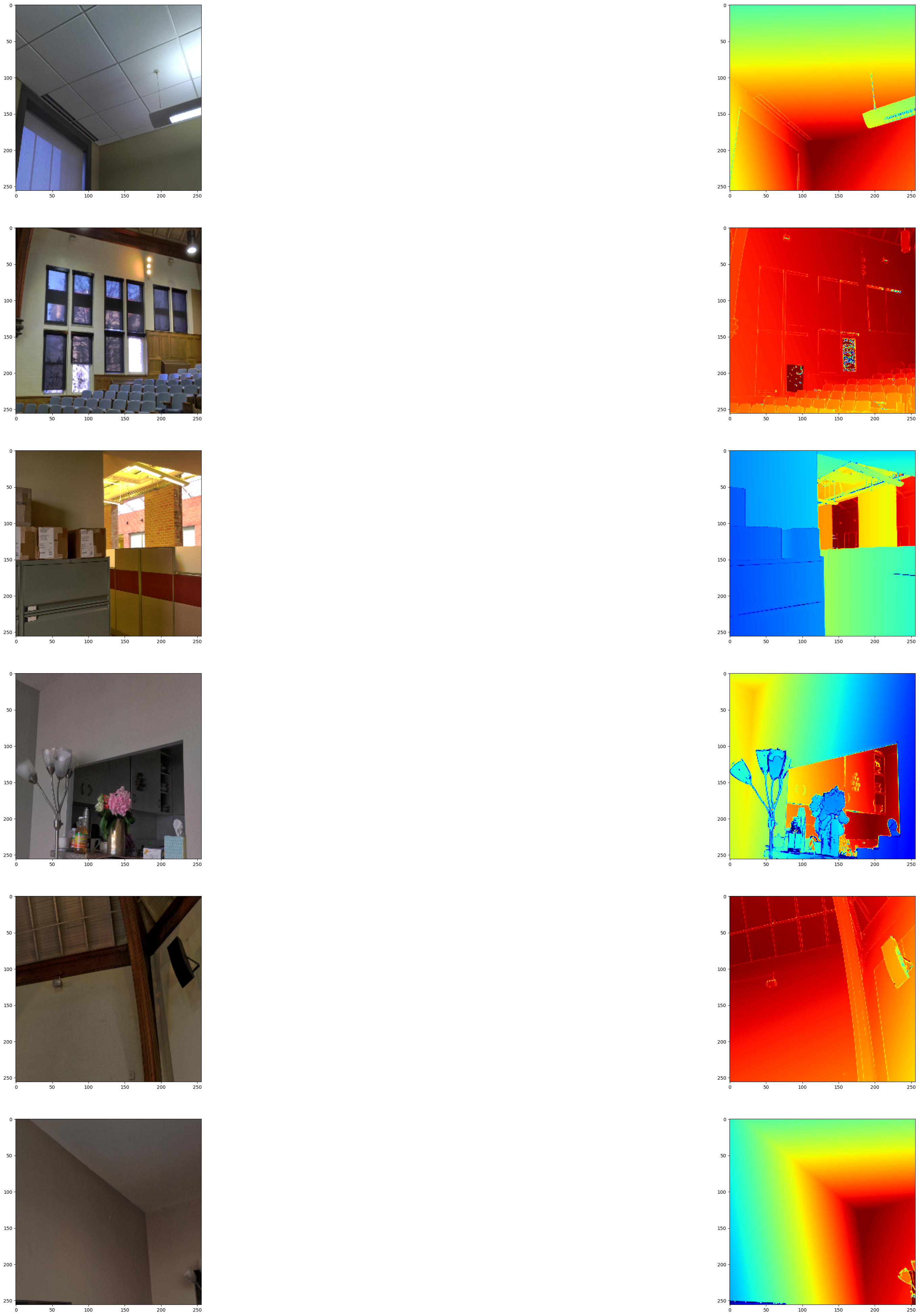
視覺化樣本
def visualize_depth_map(samples, test=False, model=None):
input, target = samples
cmap = plt.cm.jet
cmap.set_bad(color="black")
if test:
pred = model.predict(input)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(6, 3, figsize=(50, 50))
for i in range(6):
ax[i, 0].imshow((input[i].squeeze()))
ax[i, 1].imshow((target[i].squeeze()), cmap=cmap)
ax[i, 2].imshow((pred[i].squeeze()), cmap=cmap)
else:
fig, ax = plt.subplots(6, 2, figsize=(50, 50))
for i in range(6):
ax[i, 0].imshow((input[i].squeeze()))
ax[i, 1].imshow((target[i].squeeze()), cmap=cmap)
visualize_samples = next(
iter(DataGenerator(data=df, batch_size=6, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)))
)
visualize_depth_map(visualize_samples)
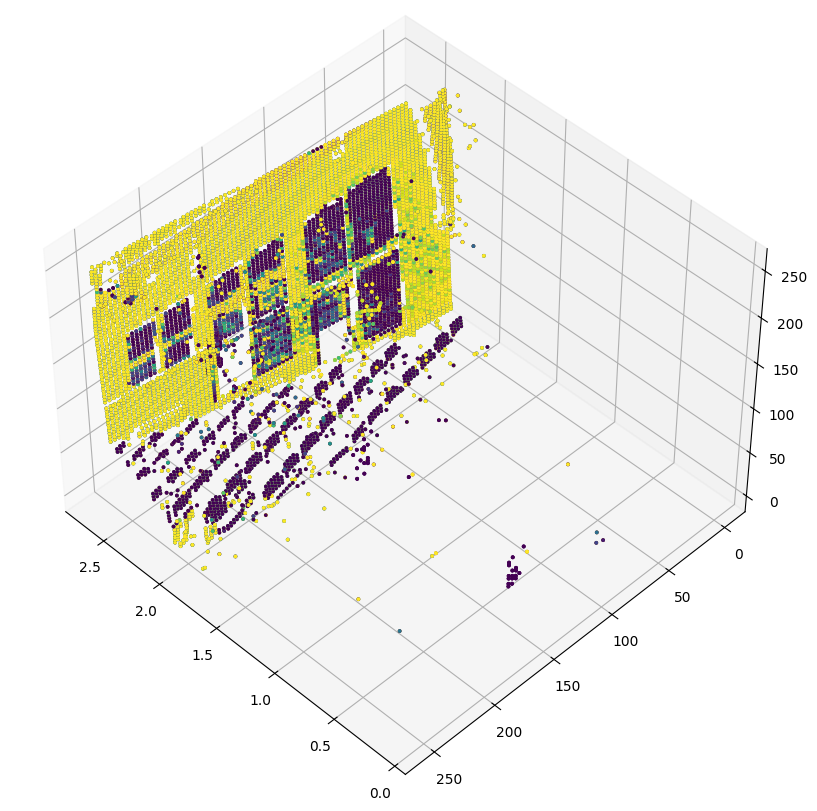
3D 點雲視覺化
depth_vis = np.flipud(visualize_samples[1][1].squeeze()) # target
img_vis = np.flipud(visualize_samples[0][1].squeeze()) # input
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15, 10))
ax = plt.axes(projection="3d")
STEP = 3
for x in range(0, img_vis.shape[0], STEP):
for y in range(0, img_vis.shape[1], STEP):
ax.scatter(
[depth_vis[x, y]] * 3,
[y] * 3,
[x] * 3,
c=tuple(img_vis[x, y, :3] / 255),
s=3,
)
ax.view_init(45, 135)
建構模型
- 基本模型來自 U-Net。
- 在縮減比例區塊中實作了加法式跳躍連接。
class DownscaleBlock(layers.Layer):
def __init__(
self, filters, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", strides=1, **kwargs
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.convA = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)
self.convB = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)
self.reluA = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)
self.reluB = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)
self.bn2a = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.bn2b = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.pool = layers.MaxPool2D((2, 2), (2, 2))
def call(self, input_tensor):
d = self.convA(input_tensor)
x = self.bn2a(d)
x = self.reluA(x)
x = self.convB(x)
x = self.bn2b(x)
x = self.reluB(x)
x += d
p = self.pool(x)
return x, p
class UpscaleBlock(layers.Layer):
def __init__(
self, filters, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", strides=1, **kwargs
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.us = layers.UpSampling2D((2, 2))
self.convA = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)
self.convB = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)
self.reluA = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)
self.reluB = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)
self.bn2a = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.bn2b = layers.BatchNormalization()
self.conc = layers.Concatenate()
def call(self, x, skip):
x = self.us(x)
concat = self.conc([x, skip])
x = self.convA(concat)
x = self.bn2a(x)
x = self.reluA(x)
x = self.convB(x)
x = self.bn2b(x)
x = self.reluB(x)
return x
class BottleNeckBlock(layers.Layer):
def __init__(
self, filters, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding="same", strides=1, **kwargs
):
super().__init__(**kwargs)
self.convA = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)
self.convB = layers.Conv2D(filters, kernel_size, strides, padding)
self.reluA = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)
self.reluB = layers.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.2)
def call(self, x):
x = self.convA(x)
x = self.reluA(x)
x = self.convB(x)
x = self.reluB(x)
return x
定義損失
我們將在我們的模式中優化 3 種損失。1. 結構相似性指數 (SSIM)。2. L1 損失或我們案例中的點狀深度。3. 深度平滑度損失。
在三種損失函數中,SSIM 對於改善模型效能貢獻最大。
def image_gradients(image):
if len(ops.shape(image)) != 4:
raise ValueError(
"image_gradients expects a 4D tensor "
"[batch_size, h, w, d], not {}.".format(ops.shape(image))
)
image_shape = ops.shape(image)
batch_size, height, width, depth = ops.unstack(image_shape)
dy = image[:, 1:, :, :] - image[:, :-1, :, :]
dx = image[:, :, 1:, :] - image[:, :, :-1, :]
# Return tensors with same size as original image by concatenating
# zeros. Place the gradient [I(x+1,y) - I(x,y)] on the base pixel (x, y).
shape = ops.stack([batch_size, 1, width, depth])
dy = ops.concatenate([dy, ops.zeros(shape, dtype=image.dtype)], axis=1)
dy = ops.reshape(dy, image_shape)
shape = ops.stack([batch_size, height, 1, depth])
dx = ops.concatenate([dx, ops.zeros(shape, dtype=image.dtype)], axis=2)
dx = ops.reshape(dx, image_shape)
return dy, dx
class DepthEstimationModel(keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.ssim_loss_weight = 0.85
self.l1_loss_weight = 0.1
self.edge_loss_weight = 0.9
self.loss_metric = keras.metrics.Mean(name="loss")
f = [16, 32, 64, 128, 256]
self.downscale_blocks = [
DownscaleBlock(f[0]),
DownscaleBlock(f[1]),
DownscaleBlock(f[2]),
DownscaleBlock(f[3]),
]
self.bottle_neck_block = BottleNeckBlock(f[4])
self.upscale_blocks = [
UpscaleBlock(f[3]),
UpscaleBlock(f[2]),
UpscaleBlock(f[1]),
UpscaleBlock(f[0]),
]
self.conv_layer = layers.Conv2D(1, (1, 1), padding="same", activation="tanh")
def calculate_loss(self, target, pred):
# Edges
dy_true, dx_true = image_gradients(target)
dy_pred, dx_pred = image_gradients(pred)
weights_x = ops.cast(ops.exp(ops.mean(ops.abs(dx_true))), "float32")
weights_y = ops.cast(ops.exp(ops.mean(ops.abs(dy_true))), "float32")
# Depth smoothness
smoothness_x = dx_pred * weights_x
smoothness_y = dy_pred * weights_y
depth_smoothness_loss = ops.mean(abs(smoothness_x)) + ops.mean(
abs(smoothness_y)
)
# Structural similarity (SSIM) index
ssim_loss = ops.mean(
1
- tf.image.ssim(
target, pred, max_val=WIDTH, filter_size=7, k1=0.01**2, k2=0.03**2
)
)
# Point-wise depth
l1_loss = ops.mean(ops.abs(target - pred))
loss = (
(self.ssim_loss_weight * ssim_loss)
+ (self.l1_loss_weight * l1_loss)
+ (self.edge_loss_weight * depth_smoothness_loss)
)
return loss
@property
def metrics(self):
return [self.loss_metric]
def train_step(self, batch_data):
input, target = batch_data
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
pred = self(input, training=True)
loss = self.calculate_loss(target, pred)
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, self.trainable_variables)
self.optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, self.trainable_variables))
self.loss_metric.update_state(loss)
return {
"loss": self.loss_metric.result(),
}
def test_step(self, batch_data):
input, target = batch_data
pred = self(input, training=False)
loss = self.calculate_loss(target, pred)
self.loss_metric.update_state(loss)
return {
"loss": self.loss_metric.result(),
}
def call(self, x):
c1, p1 = self.downscale_blocks[0](x)
c2, p2 = self.downscale_blocks[1](p1)
c3, p3 = self.downscale_blocks[2](p2)
c4, p4 = self.downscale_blocks[3](p3)
bn = self.bottle_neck_block(p4)
u1 = self.upscale_blocks[0](bn, c4)
u2 = self.upscale_blocks[1](u1, c3)
u3 = self.upscale_blocks[2](u2, c2)
u4 = self.upscale_blocks[3](u3, c1)
return self.conv_layer(u4)
模型訓練
optimizer = keras.optimizers.SGD(
learning_rate=LR,
nesterov=False,
)
model = DepthEstimationModel()
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer)
train_loader = DataGenerator(
data=df[:260].reset_index(drop="true"), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)
)
validation_loader = DataGenerator(
data=df[260:].reset_index(drop="true"), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)
)
model.fit(
train_loader,
epochs=EPOCHS,
validation_data=validation_loader,
)
Epoch 1/30
9/9 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 64s 5s/step - loss: 0.7656 - val_loss: 0.7738
Epoch 10/30
9/9 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 7s 602ms/step - loss: 0.7005 - val_loss: 0.6696
Epoch 20/30
9/9 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 7s 632ms/step - loss: 0.5827 - val_loss: 0.5821
Epoch 30/30
9/9 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 7s 593ms/step - loss: 0.6218 - val_loss: 0.5132
<keras.src.callbacks.history.History at 0x7f5a2886d210>
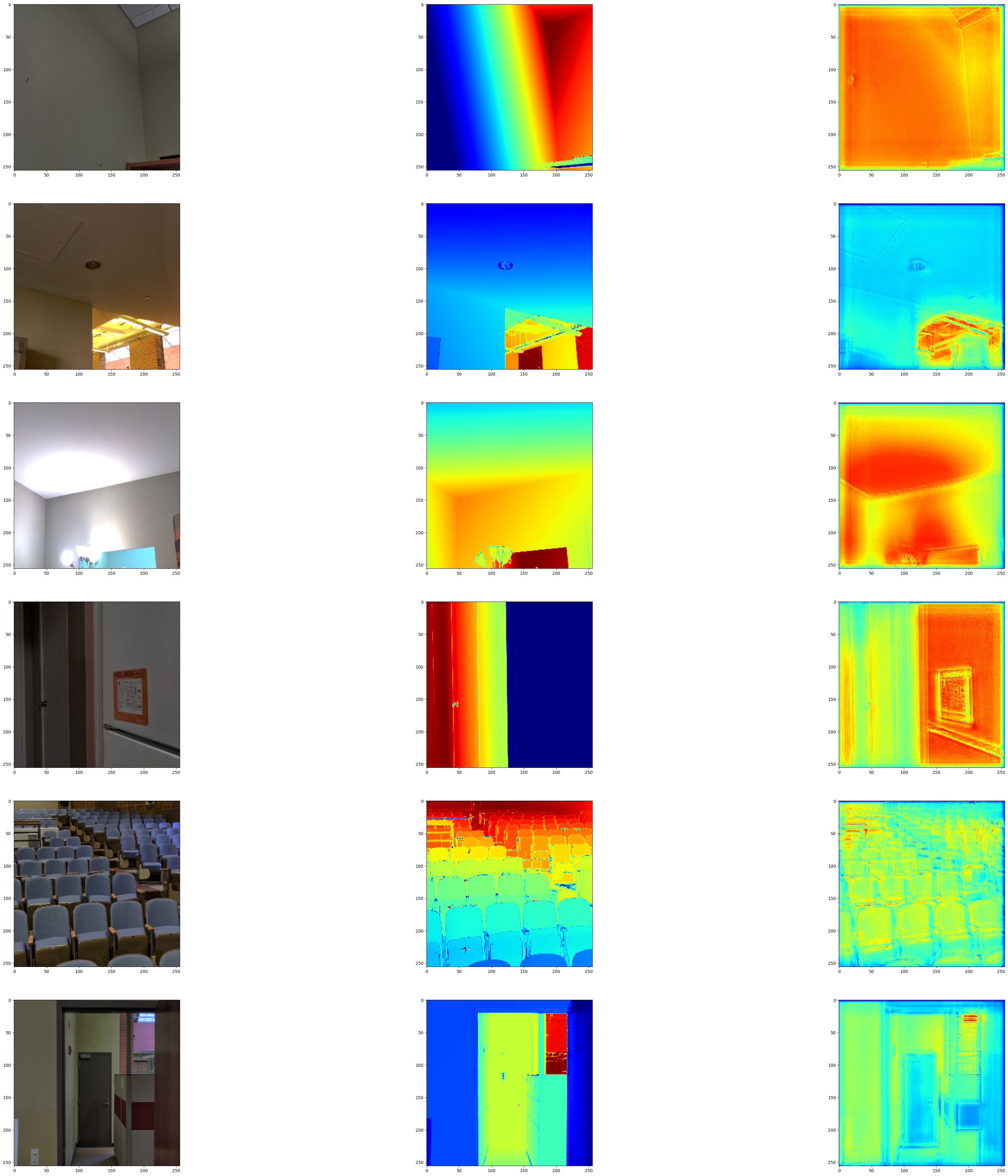
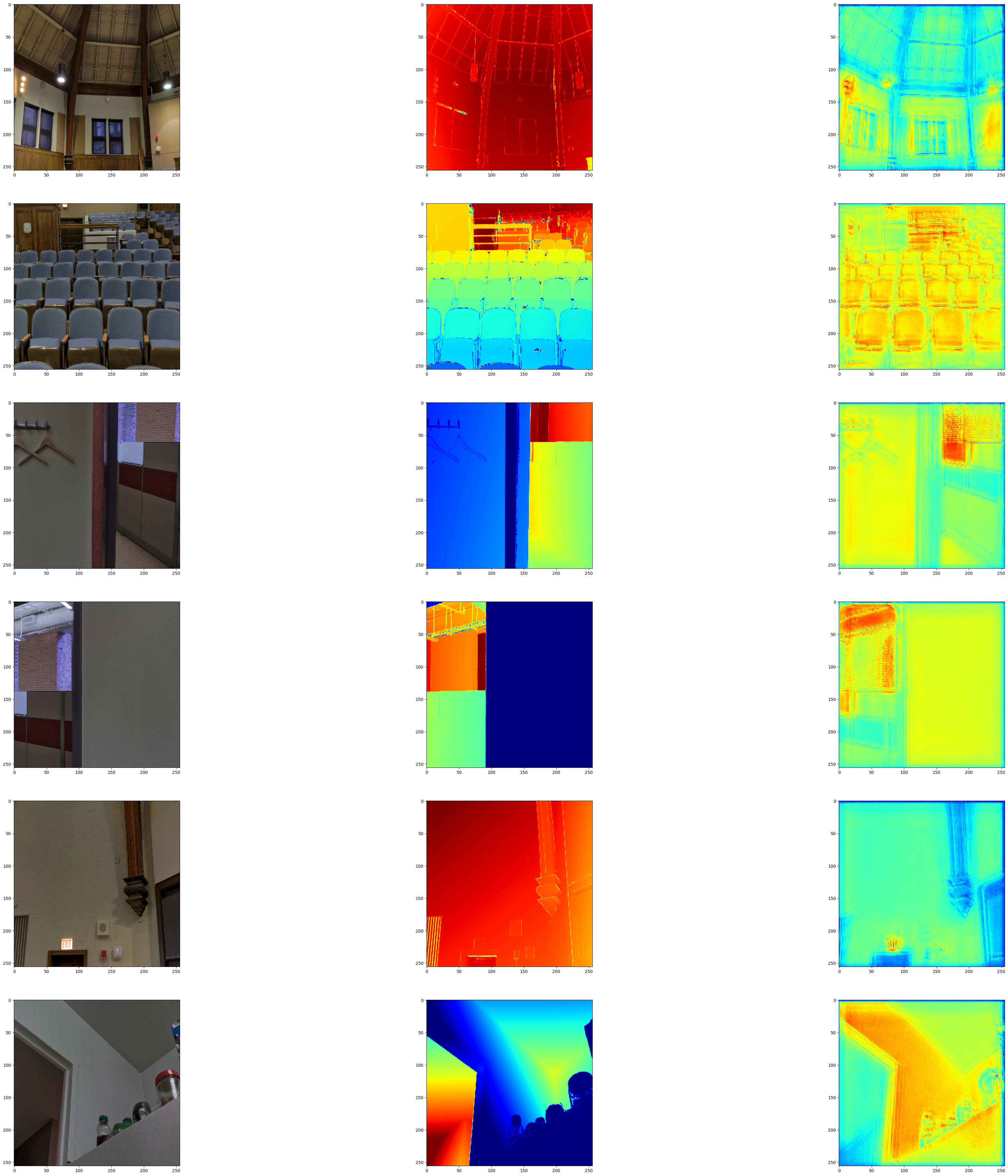
視覺化模型輸出
我們將模型輸出視覺化在驗證集上。第一張圖像為 RGB 圖像,第二張圖像為地面實況深度圖圖像,第三張為預測深度圖圖像。
test_loader = next(
iter(
DataGenerator(
data=df[265:].reset_index(drop="true"), batch_size=6, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)
)
)
)
visualize_depth_map(test_loader, test=True, model=model)
test_loader = next(
iter(
DataGenerator(
data=df[300:].reset_index(drop="true"), batch_size=6, dim=(HEIGHT, WIDTH)
)
)
)
visualize_depth_map(test_loader, test=True, model=model)
1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 781ms/step
1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 1s 782ms/step
1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 171ms/step
1/1 ━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━━ 0s 172ms/step
可能的改進
- 您可以透過將 U-Net 的編碼部分替換為預訓練的 DenseNet 或 ResNet 來改進此模型。
- 損失函數在解決此問題中扮演重要角色。調整損失函數可能會產生顯著的改進。
參考資料
以下論文深入探討了深度估計的可能方法。1. 無需感測器的深度預測:利用結構從單眼影片進行無監督學習 2. 深入探討自我監督的單眼深度估計 3. 使用全卷積殘差網路進行更深的深度預測
您也可以在帶有程式碼的深度估計任務論文中找到有用的實作。
您可以使用託管在 Hugging Face Hub 上的訓練模型,並在 Hugging Face Spaces 上試用示範。
