在 KerasHub 中分割任何物件
作者: Tirth Patel、Ian Stenbit、Divyashree Sreepathihalli
建立日期 2024/10/1
最後修改日期 2024/10/1
描述: 在 KerasHub 中使用文字、方塊和點提示分割任何物件。
概述
「分割任何物件模型」(Segment Anything Model, SAM) 可從點或方塊等輸入提示產生高品質的物件遮罩,並可用於為影像中的所有物件產生遮罩。它已在包含 1,100 萬張影像和 11 億個遮罩的資料集上進行訓練,並在各種分割任務中具有強大的零樣本效能。
在本指南中,我們將展示如何使用 KerasHub 實作的 「分割任何物件模型」,並展示 TensorFlow 和 JAX 的效能提升有多強大。
首先,讓我們取得所有相依性以及用於示範的影像。
!!pip install -Uq git+https://github.com/keras-team/keras-hub.git
!!pip install -Uq keras
!!wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/facebookresearch/segment-anything/main/notebooks/images/truck.jpg
選擇你的後端
使用 Keras 3,你可以選擇使用你最愛的後端!
import os
os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = "jax"
import timeit
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import keras
from keras import ops
import keras_hub
輔助函式
讓我們定義一些輔助函式來視覺化影像、提示和分割結果。
def show_mask(mask, ax, random_color=False):
if random_color:
color = np.concatenate([np.random.random(3), np.array([0.6])], axis=0)
else:
color = np.array([30 / 255, 144 / 255, 255 / 255, 0.6])
h, w = mask.shape[-2:]
mask_image = mask.reshape(h, w, 1) * color.reshape(1, 1, -1)
ax.imshow(mask_image)
def show_points(coords, labels, ax, marker_size=375):
pos_points = coords[labels == 1]
neg_points = coords[labels == 0]
ax.scatter(
pos_points[:, 0],
pos_points[:, 1],
color="green",
marker="*",
s=marker_size,
edgecolor="white",
linewidth=1.25,
)
ax.scatter(
neg_points[:, 0],
neg_points[:, 1],
color="red",
marker="*",
s=marker_size,
edgecolor="white",
linewidth=1.25,
)
def show_box(box, ax):
box = box.reshape(-1)
x0, y0 = box[0], box[1]
w, h = box[2] - box[0], box[3] - box[1]
ax.add_patch(
plt.Rectangle((x0, y0), w, h, edgecolor="green", facecolor=(0, 0, 0, 0), lw=2)
)
def inference_resizing(image, pad=True):
# Compute Preprocess Shape
image = ops.cast(image, dtype="float32")
old_h, old_w = image.shape[0], image.shape[1]
scale = 1024 * 1.0 / max(old_h, old_w)
new_h = old_h * scale
new_w = old_w * scale
preprocess_shape = int(new_h + 0.5), int(new_w + 0.5)
# Resize the image
image = ops.image.resize(image[None, ...], preprocess_shape)[0]
# Pad the shorter side
if pad:
pixel_mean = ops.array([123.675, 116.28, 103.53])
pixel_std = ops.array([58.395, 57.12, 57.375])
image = (image - pixel_mean) / pixel_std
h, w = image.shape[0], image.shape[1]
pad_h = 1024 - h
pad_w = 1024 - w
image = ops.pad(image, [(0, pad_h), (0, pad_w), (0, 0)])
# KerasHub now rescales the images and normalizes them.
# Just unnormalize such that when KerasHub normalizes them
# again, the padded values map to 0.
image = image * pixel_std + pixel_mean
return image
取得預訓練的 SAM 模型
我們可以使用 KerasHub 的 from_preset 工廠方法初始化訓練過的 SAM 模型。在這裡,我們使用在 SA-1B 資料集上訓練的巨大 ViT 骨幹 (sam_huge_sa1b) 來取得高品質的分割遮罩。你也可以使用 sam_large_sa1b 或 sam_base_sa1b 來獲得更好的效能 (但會犧牲分割遮罩的品質)。
model = keras_hub.models.SAMImageSegmenter.from_preset("sam_huge_sa1b")
瞭解提示
「分割任何物件」允許使用點、方塊和遮罩來提示影像
- 點提示是最基本的:模型嘗試根據影像上的點來猜測物件。該點可以是前景點 (即所需的分割遮罩包含其中的點),也可以是背景點 (即該點位於所需遮罩之外)。
- 提示模型的另一種方式是使用方塊。給定一個邊界方塊,模型會嘗試分割其中包含的物件。
- 最後,也可以使用遮罩本身來提示模型。例如,這對於精煉先前預測或已知的分割遮罩的邊界很有用。
使模型功能非常強大的是能夠結合上述提示。點、方塊和遮罩提示可以多種不同的方式組合,以達到最佳結果。
讓我們看看將這些提示傳遞給 KerasHub 中「分割任何物件模型」的語義。SAM 模型的輸入是一個字典,包含以下鍵
"images":要分割的影像批次。形狀必須為(B, 1024, 1024, 3)。"points":點提示批次。每個點都是一個(x, y)座標,源自影像的左上角。換句話說,每個點的形式為(r, c),其中r和c是影像中像素的列和欄。形狀必須為(B, N, 2)。"labels":給定點的標籤批次。1代表前景點,而0代表背景點。形狀必須為(B, N)。"boxes":方塊批次。請注意,模型每個批次僅接受一個方塊。因此,預期的形狀為(B, 1, 2, 2)。每個方塊都是 2 個點的集合:方塊的左上角和右下角。此處的點遵循與點提示相同的語義。此處第二個維度中的1代表方塊提示的存在。如果缺少方塊提示,則必須傳遞形狀為(B, 0, 2, 2)的預留位置輸入。"masks":遮罩批次。與方塊提示一樣,每個影像僅允許一個遮罩提示。如果存在輸入遮罩,則其形狀必須為(B, 1, 256, 256, 1),如果缺少遮罩提示,則為(B, 0, 256, 256, 1)。
僅在直接呼叫模型時 (即 model(...)) 才需要預留位置提示。呼叫 predict 方法時,可以從輸入字典中省略缺少的提示。
點提示
首先,讓我們使用點提示分割影像。我們載入影像並將其調整為形狀 (1024, 1024),這是預訓練 SAM 模型預期的影像大小。
# Load our image
image = np.array(keras.utils.load_img("truck.jpg"))
image = inference_resizing(image)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(ops.convert_to_numpy(image) / 255.0)
plt.axis("on")
plt.show()

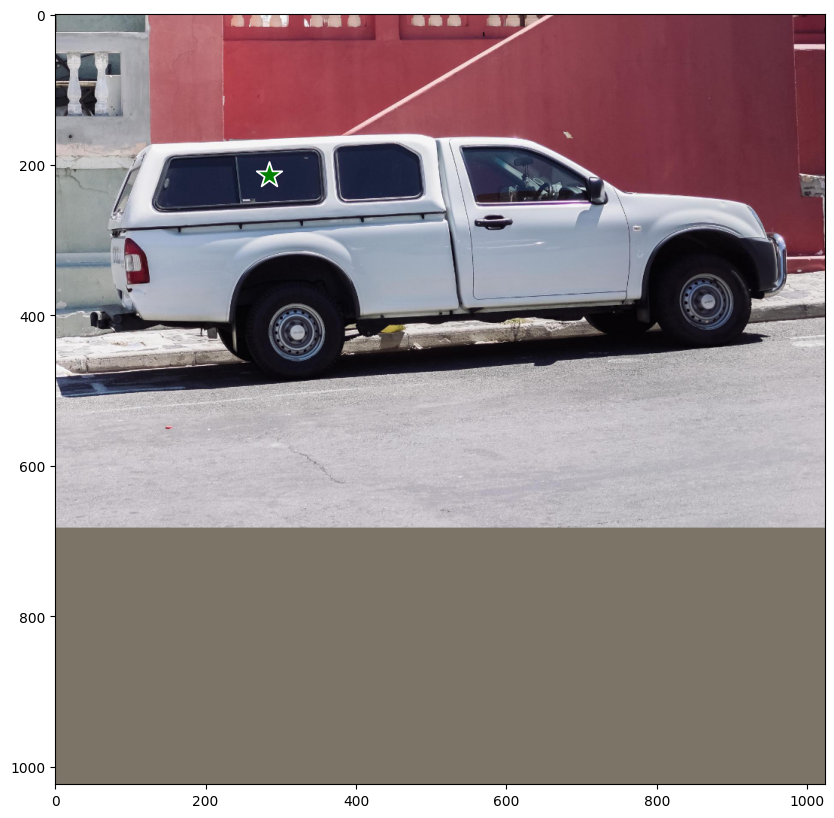
接下來,我們將定義要分割的物件上的點。讓我們嘗試分割座標 (284, 213) 處卡車的窗玻璃。
# Define the input point prompt
input_point = np.array([[284, 213.5]])
input_label = np.array([1])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(ops.convert_to_numpy(image) / 255.0)
show_points(input_point, input_label, plt.gca())
plt.axis("on")
plt.show()

現在讓我們呼叫我們模型的 predict 方法來取得分割遮罩。
注意:我們不會直接呼叫模型 (model(...)),因為這樣做需要預留位置提示。predict 方法會自動處理缺少的提示,因此我們改為呼叫它。此外,當不存在方塊提示時,點和標籤需要分別使用零點提示和 -1 標籤提示進行填補。下面的單元格示範了此功能的工作方式。
outputs = model.predict(
{
"images": image[np.newaxis, ...],
"points": np.concatenate(
[input_point[np.newaxis, ...], np.zeros((1, 1, 2))], axis=1
),
"labels": np.concatenate(
[input_label[np.newaxis, ...], np.full((1, 1), fill_value=-1)], axis=1
),
}
)
SegmentAnythingModel.predict 會傳回兩個輸出。第一個是形狀為 (1, 4, 256, 256) 的邏輯值 (分割遮罩),另一個是每個預測遮罩的 IoU 信賴分數 (形狀為 (1, 4))。預訓練的 SAM 模型會預測四個遮罩:第一個是模型針對給定提示所能提出的最佳遮罩,其他三個是替代遮罩,如果最佳預測不包含所需的物件,則可以使用這些遮罩。使用者可以選擇他們偏好的任何遮罩。
讓我們視覺化模型傳回的遮罩!
# Resize the mask to our image shape i.e. (1024, 1024)
mask = inference_resizing(outputs["masks"][0][0][..., None], pad=False)[..., 0]
# Convert the logits to a numpy array
# and convert the logits to a boolean mask
mask = ops.convert_to_numpy(mask) > 0.0
iou_score = ops.convert_to_numpy(outputs["iou_pred"][0][0])
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(ops.convert_to_numpy(image) / 255.0)
show_mask(mask, plt.gca())
show_points(input_point, input_label, plt.gca())
plt.title(f"IoU Score: {iou_score:.3f}", fontsize=18)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
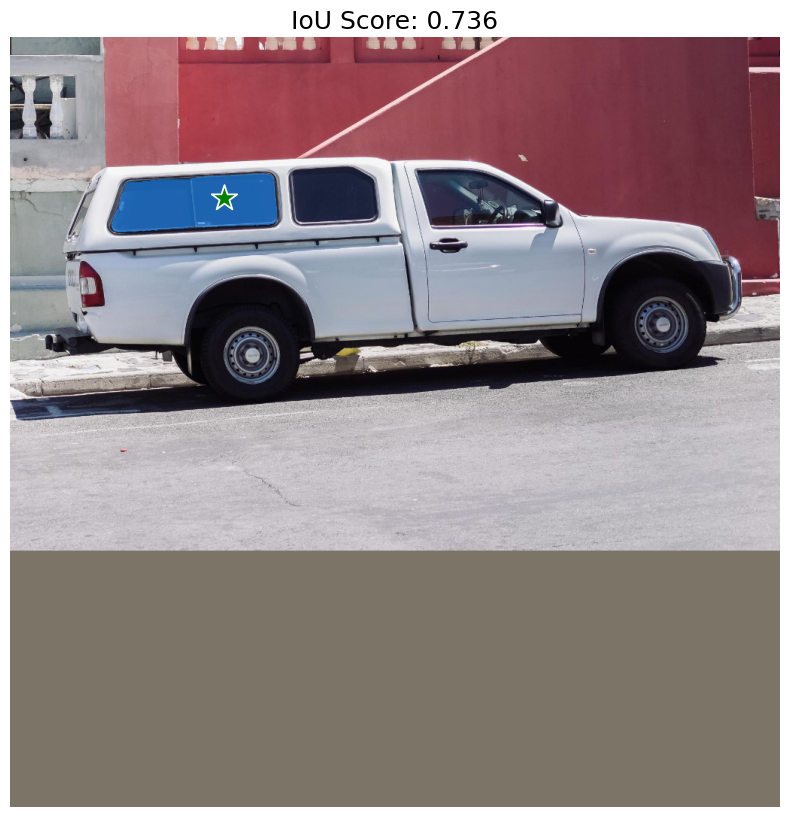

如預期的那樣,模型傳回了卡車窗玻璃的分割遮罩。但是,我們的點提示也可能意味著其他各種事物。例如,另一個包含我們點的可能遮罩只是窗玻璃的右側或整輛卡車。
讓我們也視覺化模型預測的其他遮罩。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(20, 60))
masks, scores = outputs["masks"][0][1:], outputs["iou_pred"][0][1:]
for i, (mask, score) in enumerate(zip(masks, scores)):
mask = inference_resizing(mask[..., None], pad=False)[..., 0]
mask, score = map(ops.convert_to_numpy, (mask, score))
mask = 1 * (mask > 0.0)
ax[i].imshow(ops.convert_to_numpy(image) / 255.0)
show_mask(mask, ax[i])
show_points(input_point, input_label, ax[i])
ax[i].set_title(f"Mask {i+1}, Score: {score:.3f}", fontsize=12)
ax[i].axis("off")
plt.show()

太棒了!SAM 能夠捕捉到我們點提示的模糊性,並且還傳回了其他可能的分割遮罩。
方塊提示
現在,讓我們看看如何使用方塊提示模型。該方塊使用兩個點來指定,即 xyxy 格式的邊界方塊的左上角和右下角。讓我們使用卡車左前輪周圍的邊界方塊來提示模型。
# Let's specify the box
input_box = np.array([[240, 340], [400, 500]])
outputs = model.predict(
{"images": image[np.newaxis, ...], "boxes": input_box[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, ...]}
)
mask = inference_resizing(outputs["masks"][0][0][..., None], pad=False)[..., 0]
mask = ops.convert_to_numpy(mask) > 0.0
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(ops.convert_to_numpy(image) / 255.0)
show_mask(mask, plt.gca())
show_box(input_box, plt.gca())
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()

成功!模型完美地分割出我們邊界方塊中的左前輪胎。
結合提示
為了發揮模型真正的潛力,讓我們結合方塊和點提示,看看模型會做什麼。
# Let's specify the box
input_box = np.array([[240, 340], [400, 500]])
# Let's specify the point and mark it background
input_point = np.array([[325, 425]])
input_label = np.array([0])
outputs = model.predict(
{
"images": image[np.newaxis, ...],
"points": input_point[np.newaxis, ...],
"labels": input_label[np.newaxis, ...],
"boxes": input_box[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, ...],
}
)
mask = inference_resizing(outputs["masks"][0][0][..., None], pad=False)[..., 0]
mask = ops.convert_to_numpy(mask) > 0.0
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(ops.convert_to_numpy(image) / 255.0)
show_mask(mask, plt.gca())
show_box(input_box, plt.gca())
show_points(input_point, input_label, plt.gca())
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
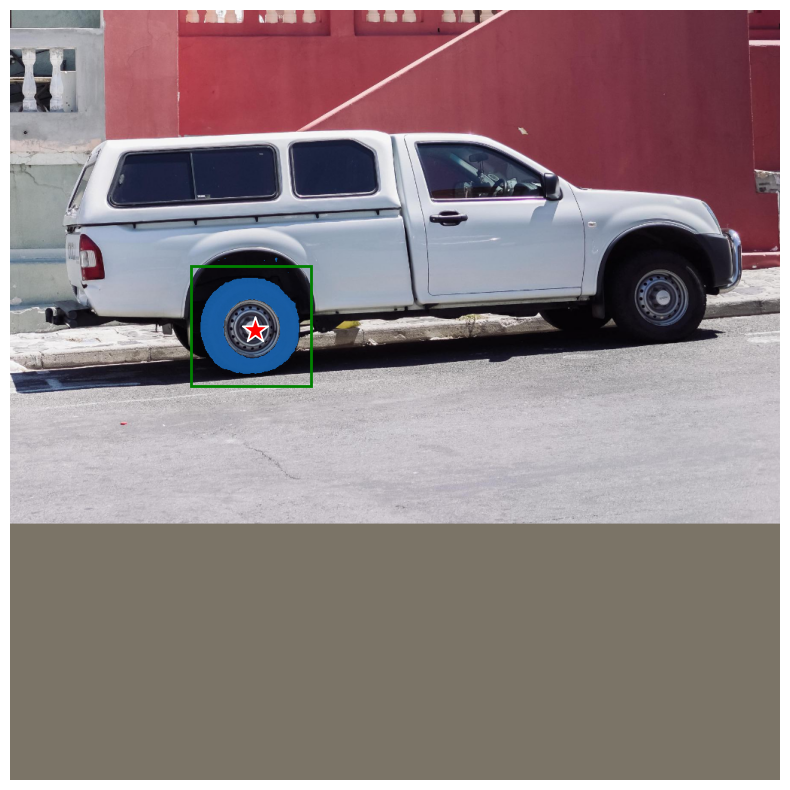

太棒了!模型瞭解到我們想要從遮罩中排除的物件是輪胎的輪圈。
文字提示
最後,讓我們看看如何將文字提示與 KerasHub 的 SegmentAnythingModel 一起使用。
在此示範中,我們將使用 官方的 Grounding DINO 模型。Grounding DINO 是一個模型,它將 (影像、文字) 對作為輸入,並在 text 所描述的 image 中物件周圍產生邊界方塊。你可以參考論文,以瞭解有關模型實作的更多詳細資訊。
對於此示範部分,我們需要從來源安裝 groundingdino 套件
pip install -U git+https://github.com/IDEA-Research/GroundingDINO.git
然後,我們可以安裝預訓練模型的權重和組態
!!pip install -U git+https://github.com/IDEA-Research/GroundingDINO.git
!!wget -q https://github.com/IDEA-Research/GroundingDINO/releases/download/v0.1.0-alpha/groundingdino_swint_ogc.pth
!!wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/IDEA-Research/GroundingDINO/v0.1.0-alpha2/groundingdino/config/GroundingDINO_SwinT_OGC.py
from groundingdino.util.inference import Model as GroundingDINO
CONFIG_PATH = "GroundingDINO_SwinT_OGC.py"
WEIGHTS_PATH = "groundingdino_swint_ogc.pth"
grounding_dino = GroundingDINO(CONFIG_PATH, WEIGHTS_PATH)
讓我們為這部分載入一張狗的影像!
filepath = keras.utils.get_file(
origin="https://storage.googleapis.com/keras-cv/test-images/mountain-dog.jpeg"
)
image = np.array(keras.utils.load_img(filepath))
image = ops.convert_to_numpy(inference_resizing(image))
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(image / 255.0)
plt.axis("on")
plt.show()
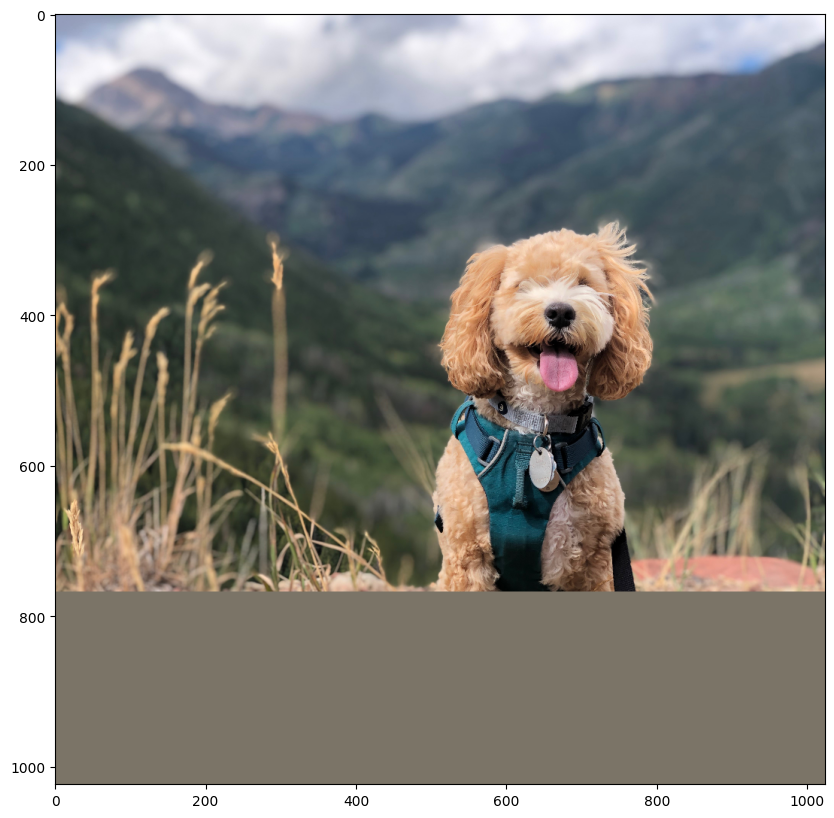
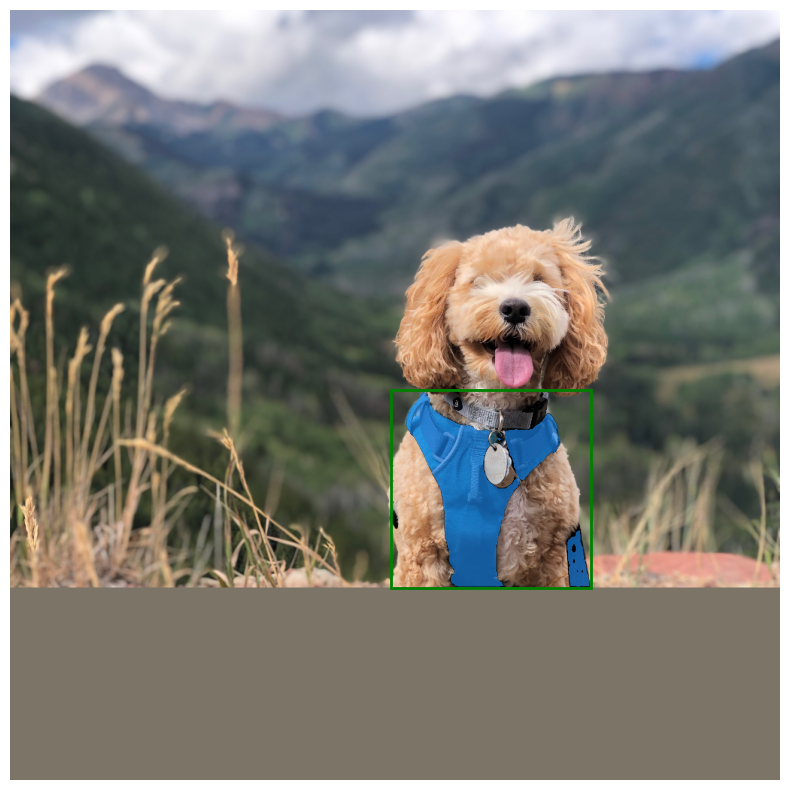
我們首先使用 Grounding DINO 模型預測我們想要分割的物件的邊界方塊。然後,我們使用邊界方塊提示 SAM 模型以取得分割遮罩。
讓我們嘗試分割狗的胸背帶。變更以下影像和文字,以便使用影像中的文字分割任何你想要分割的內容!
# Let's predict the bounding box for the harness of the dog
boxes = grounding_dino.predict_with_caption(image.astype(np.uint8), "harness")
boxes = np.array(boxes[0].xyxy)
outputs = model.predict(
{
"images": np.repeat(image[np.newaxis, ...], boxes.shape[0], axis=0),
"boxes": boxes.reshape(-1, 1, 2, 2),
},
batch_size=1,
)
就是這樣!我們使用 Gounding DINO + SAM 的組合,取得了文字提示的分割遮罩!這是結合不同模型以擴展應用程式的非常強大的技術!
讓我們視覺化結果。
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(image / 255.0)
for mask in outputs["masks"]:
mask = inference_resizing(mask[0][..., None], pad=False)[..., 0]
mask = ops.convert_to_numpy(mask) > 0.0
show_mask(mask, plt.gca())
show_box(boxes, plt.gca())
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()

最佳化 SAM
你可以使用 mixed_float16 或 bfloat16 dtype 原則,以相對較低的精度損失來獲得巨大的速度提升和記憶體最佳化。
# Load our image
image = np.array(keras.utils.load_img("truck.jpg"))
image = inference_resizing(image)
# Specify the prompt
input_box = np.array([[240, 340], [400, 500]])
# Let's first see how fast the model is with float32 dtype
time_taken = timeit.repeat(
'model.predict({"images": image[np.newaxis, ...], "boxes": input_box[np.newaxis, np.newaxis, ...]}, verbose=False)',
repeat=3,
number=3,
globals=globals(),
)
print(f"Time taken with float32 dtype: {min(time_taken) / 3:.10f}s")
# Set the dtype policy in Keras
keras.mixed_precision.set_global_policy("mixed_float16")
model = keras_hub.models.SAMImageSegmenter.from_preset("sam_huge_sa1b")
time_taken = timeit.repeat(
'model.predict({"images": image[np.newaxis, ...], "boxes": input_box[np.newaxis,np.newaxis, ...]}, verbose=False)',
repeat=3,
number=3,
globals=globals(),
)
print(f"Time taken with float16 dtype: {min(time_taken) / 3:.10f}s")
以下是 KerasHub 實作與原始 PyTorch 實作的比較!
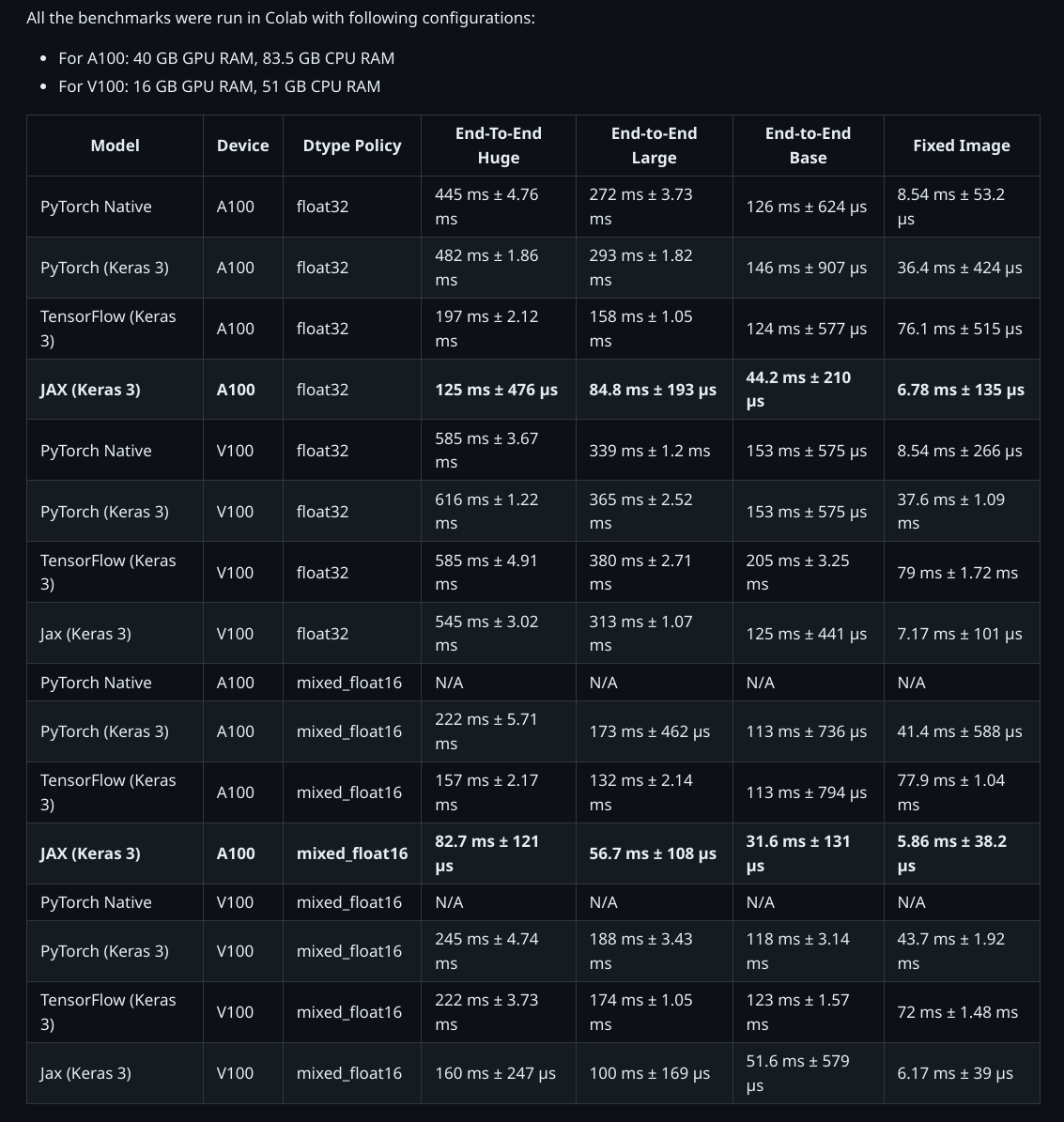
用於產生基準測試的指令碼位於此處。
結論
KerasHub 的 SegmentAnythingModel 支援各種應用程式,並借助 Keras 3,可以在 TensorFlow、JAX 和 PyTorch 上執行模型!借助 JAX 和 TensorFlow 中的 XLA,模型的執行速度比原始實作快數倍。此外,使用 Keras 的混合精度支援僅需一行程式碼即可最佳化記憶體使用和計算時間!
如需更多進階用法,請查看自動遮罩產生器示範。
